
Instructional Goal: Students will know the major geographical characteristics of Mesopotamia and understand their impact on the formation of civilization.
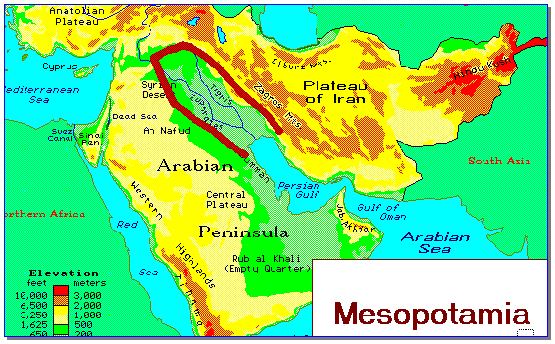
- A civilization developed in an area that came to be known as Mesopotamia.
- Mesopotamia means, "Land between the rivers".
- Civilization developed between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in present-day Iraq and Kuwait.
- Mesopotamia is further divided into an upper and lower region.
- The upper area was known as Akkad and was characterized by a fertile plain.
- The lower region was known as Sumer and was made up of swamps along the delta area where the rivers emptied into the Persian Gulf.
- Civilization developed in Mesopotamia simultaneously with Egypt and the two are often called the "Fertile Crescent". The Tigris and Euphrates rivers, however, had a different impact on the development of civilization than the Nile had on Egypt.
Mesopotamia did not have protection from natural boundaries.
- This led to constant migrations of Indo-European people from the area between the Black and Caspian seas.
- This constant migration led to "Cultural Diffusion", or the process where an existing culture adopts the traits of another and the two eventually merge into a new culture.
- As a result, a strong central government failed to develop in Mesopotamia.
- The dominant political unit was the "city-state", a small area surrounding a large, complex city.
- The climate is exceedingly hot, but also very humid.
- The floods of the Tigris and Euphrates were very violent and unpredictable.
Assignment: students will begin work on map of Mesopotamia


